What is prominent ear?
Prominent ears are a condition where the ear project outward and forward from the head, making the outer ears visible when viewed from the front. Medically, prominent ears are defined when the helical–mastoid distance exceeds 2cm. This condition negatively affects facial aesthetics.

Before and after ear pinning treatments
What causes prominent ears?
- There are two main causes:
- Underdevelopment or incomplete development of the antihelical fold, resulting in a flattened or absent antihelical fold.
- Unusual deeper conchal bowl
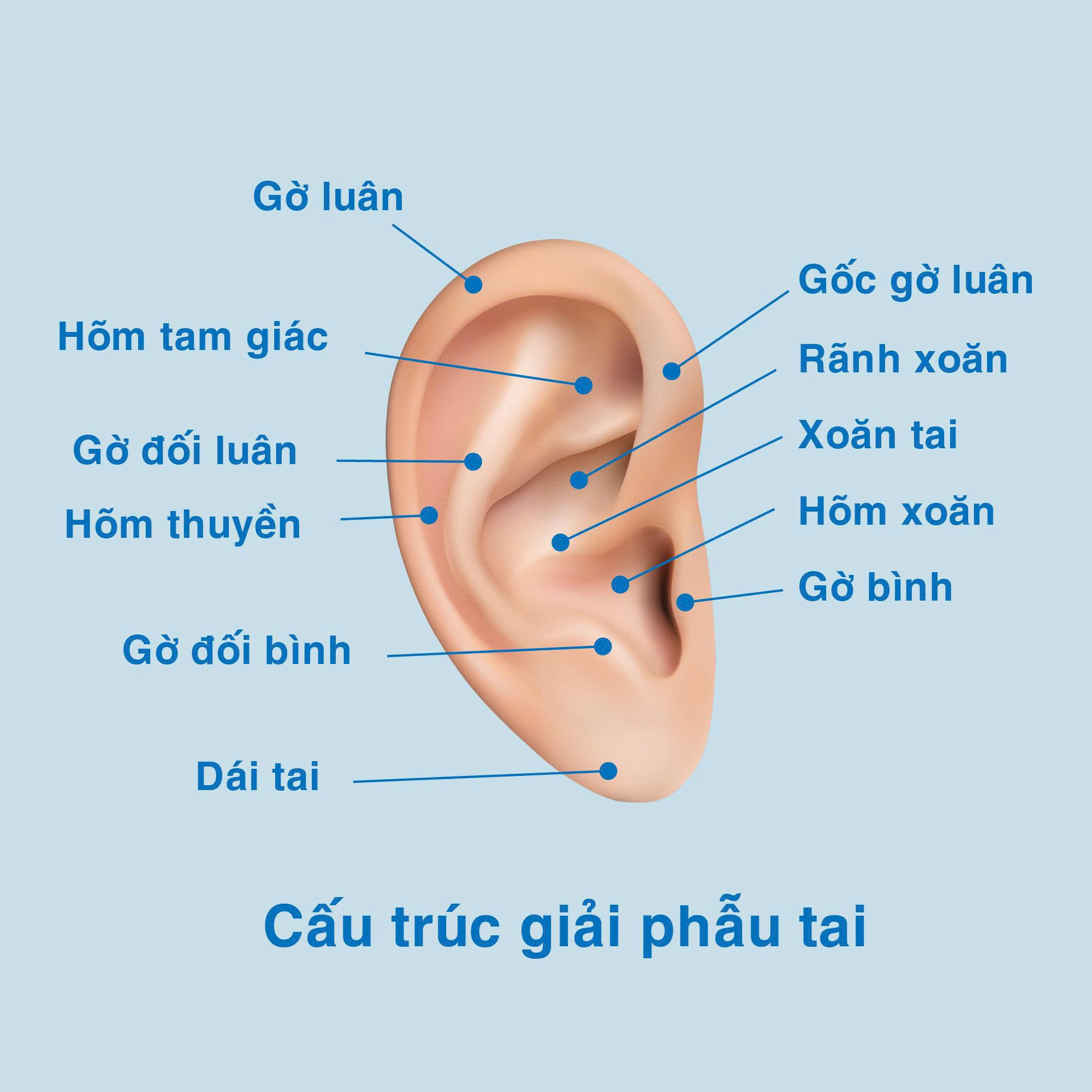
Ear anatomy
Underdevelopment of the antihelical fold accounts for up to 70% of cases. Therefore, most treatment methods focus on creating or defining the antihelical fold..
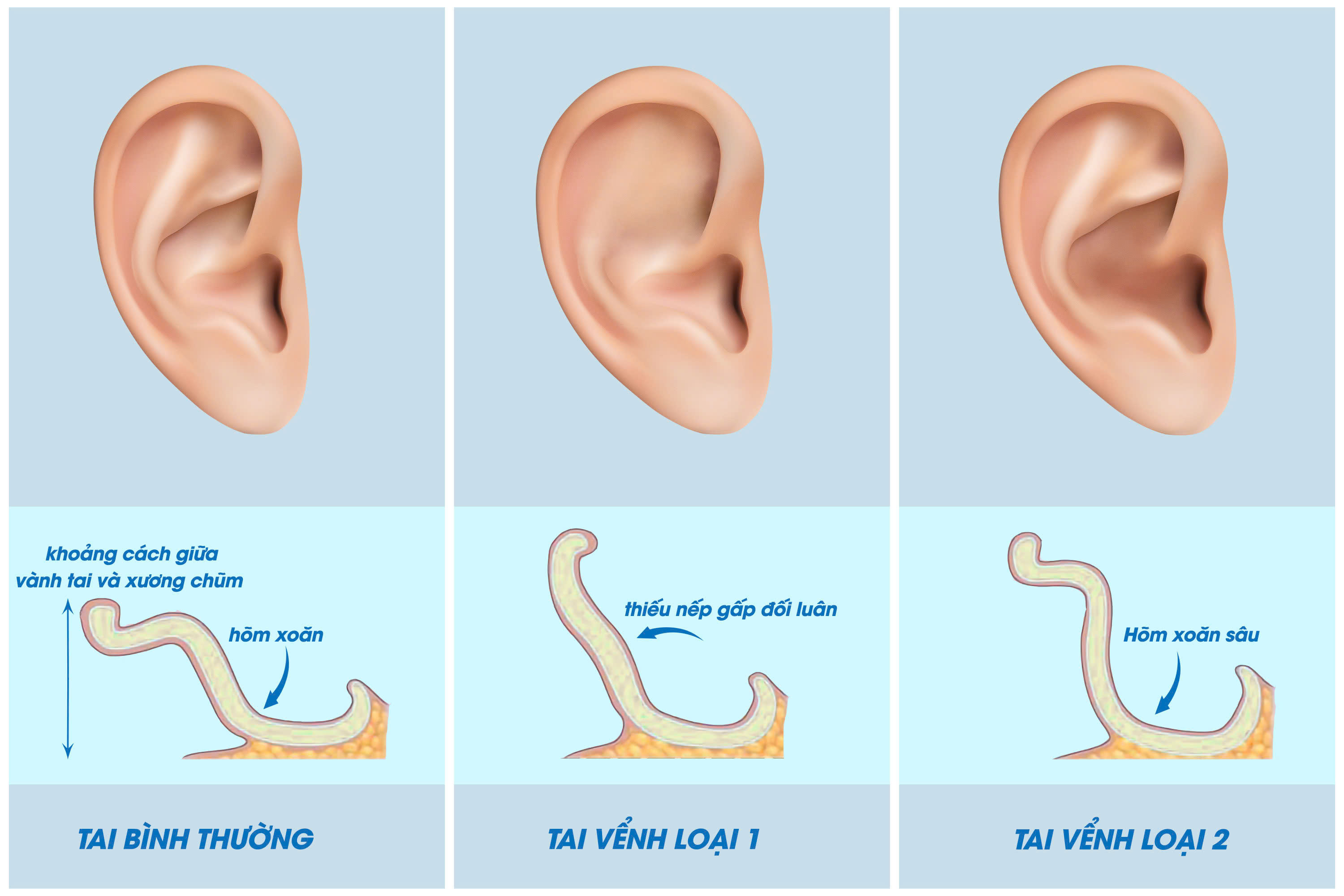
Comparing between prominent ears causes and normal ears
Indication?
This surgery is suitable for patients who wish to change their ear shape, primarily those with congenital prominent ears seeking to improve their facial appearance. However, this procedure is not recommended for children under 15 years old, as the ears have not yet fully developed, as well as for patients with medical conditions that may affect the healing process, such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes.

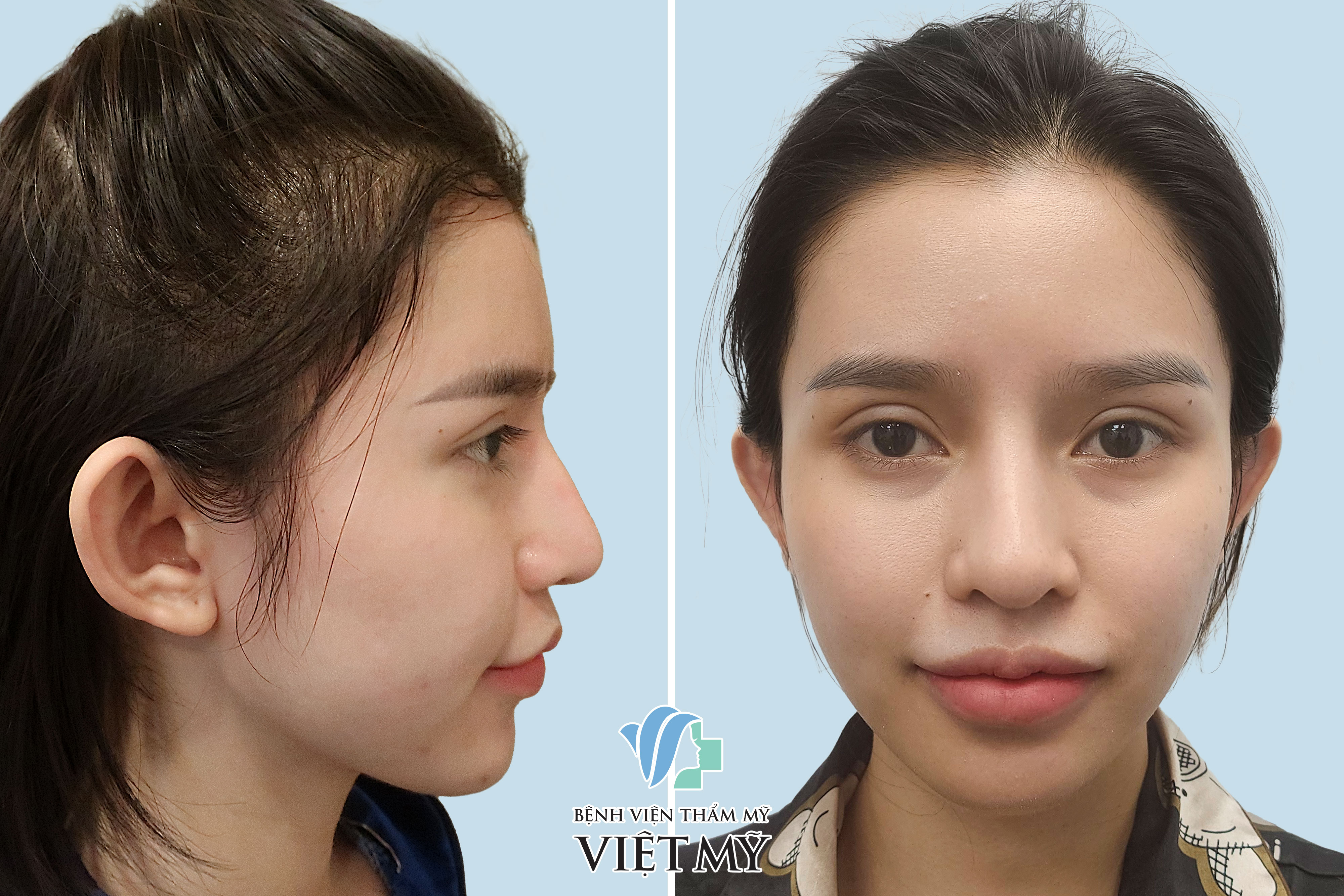
Before and after images of patient undergoing Ear Pinning treatments
What are the benefits of ear pinning surgery?
Ear pinning surgery creates a more balanced and harmonious ear shape in proportion to the face, significantly improving the patient's appearance. In most cases, long-term satisfaction with the improved appearance and increased self-confidence provides substantial mental health benefits for patients.
There are three major approaches:
1. Creating the antihelical fold using posterior sutures: The surgeon uses sutures to create a natural fold for the ear. This is the easiest method to perform with relatively quick recovery time. However, the results may not be long-lasting as sutures can loosen over time, leading to the risk of recurrence of prominent ears and the need for revision surgery.
2. Conventional cartilage-sculpting technique: A small incision is made behind the ear, on the opposite side of the antihelix. Through this incision, the surgeon removes excess cartilage, skin, and ear tissue to reduce ear prominence, then closes the incision with sutures.
3. Implant method combined with conchal bowl resection: Similar to the method above, the surgeon removes a portion of excess cartilage and tissue in the conchal area combined with the standard implant placement method.
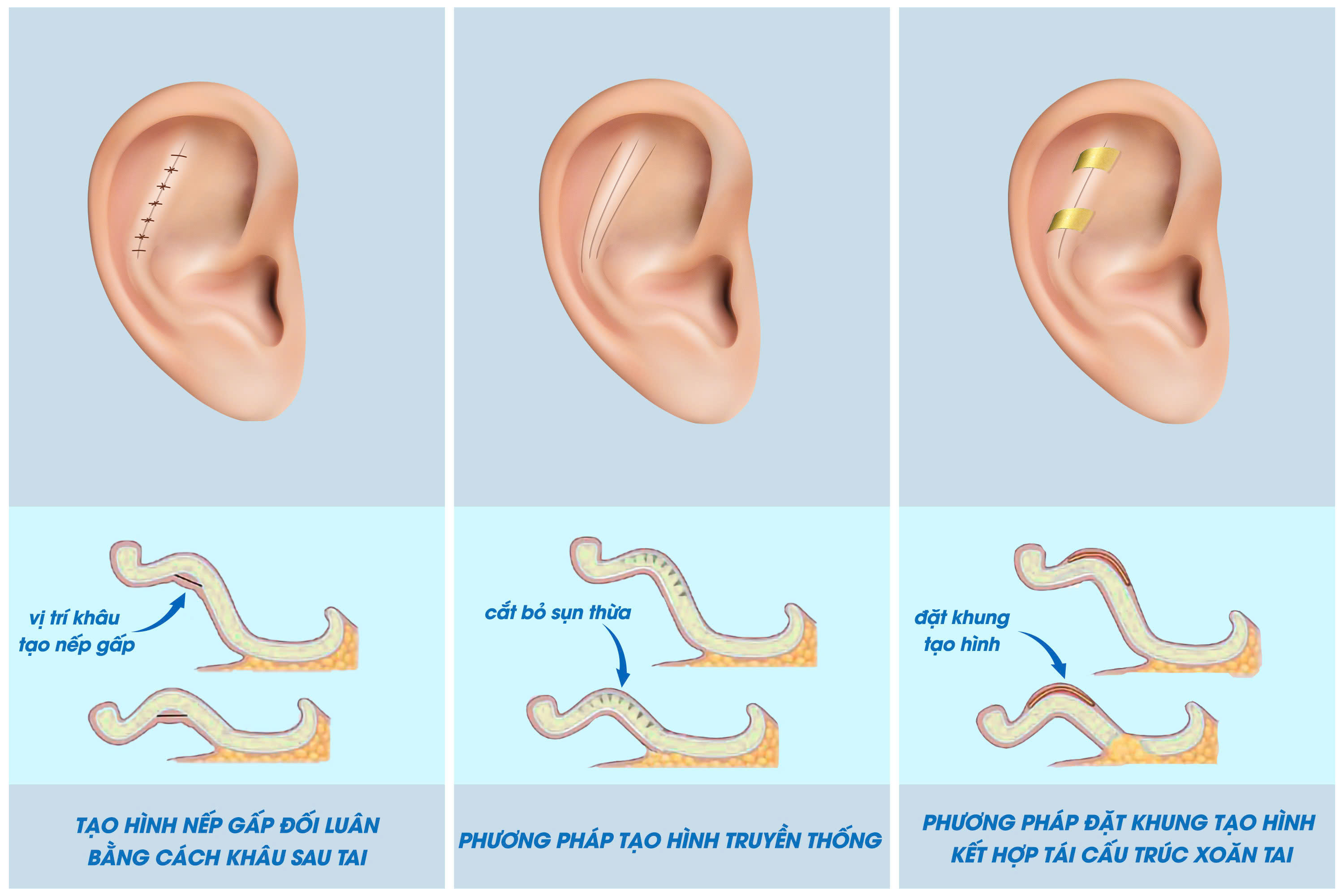
The main treatment methods
Treatment procedure and preoperative preparation
First, the surgeon will conduct an examination to assess the patient's condition and review their medical history. General health assessments and laboratory tests will be performed. The surgeon will then discuss the patient's expectations and develop a treatment plan, as well as provide preoperative preparation instructions. Patients may be required to temporarily discontinue certain anticoagulant medications or medications that may affect the healing process during this period.
The surgical procedure includes administering anesthesia or sedation, followed by performing the method outlined in the treatment plan. Incisions will be closed with sutures and medical adhesive strips.
Postoperative care and recovery
Patients will go through several stages of recovery. In the first few days after surgery, the treated area will typically experience mild swelling and bruising, which will gradually subside after two weeks. Sutures will be removed after 10 days.
However, to ensure the most effective and speedy recovery process, please follow the surgeon's postoperative care instructions, including:
- Adhere to the wound cleaning protocol.
- Avoid touching or putting pressure on the incision. Refrain from wearing glasses, headphones, or any items that may put pressure on the ears during this period.
- For optimal scar healing, limit sun exposure; when going outdoors, use protective clothing and cover the area.
- Avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting during this time.
Risk
Ear pinning surgery is generally safe; however, complications may still occur:
- Common surgical complications such as bleeding and infection.
- Discomfort or loss of sensation in the ear (rare).
- Unsatisfactory results.
The above risks are largely due to the complexity of the treated area, as the procedure is performed on thin skin with a high density of nerves and blood vessels. However, these are all avoidable risks if the surgery is performed by an experienced surgeon at a facility equipped with specialized devices to support all stages of the procedure.
* The final results also depend on individual's physiology.